Meaning Definition Law Of Demand
/Supplyrelationship-c0f71135bc884f4b8e5d063eed128b52.png)
Meaning of law of demand.
Meaning definition law of demand. Law of demand definition. Law of demand definition is a statement in economics. Let s understand this clearly.
Information and translations of law of demand in the most comprehensive dictionary definitions resource on the web. The law of demand affirms the inverse relationship between price and demand. The law of demand assumes that all determinants of demand except price remains unchanged.
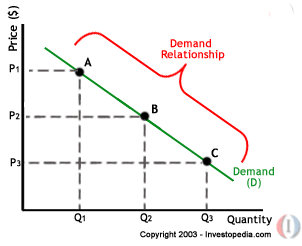
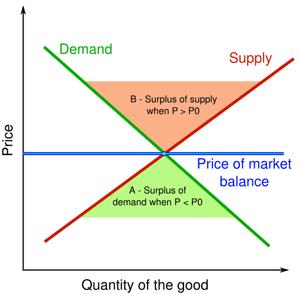
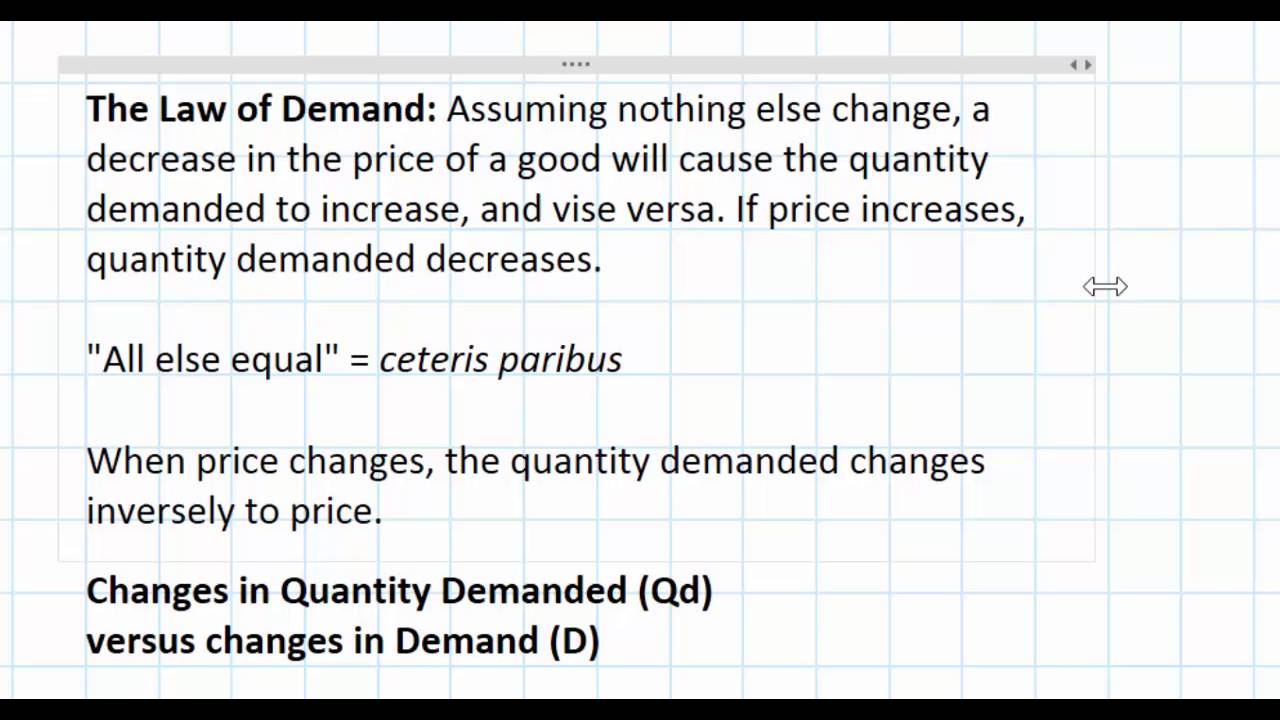
Conversely a price decrease increases its demand. In the market assuming other factors affecting. The law of demand is the concept of the economics according to which the prices of the goods or services and their quantity demanded is inversely related to each other when the other factors remain constant.
The law of demand is a microeconomic concept that states that when the price of a product decreases consumer demand for this particular product increases provided that all other factors that affect consumer demand remain equal ceteris paribus. When price rises a good or service becomes less desirable. In other words the higher the price the lower the quantity demanded.
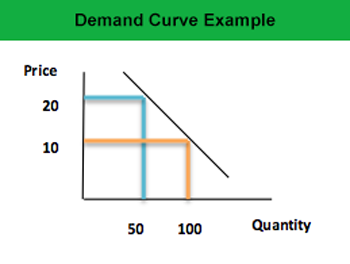
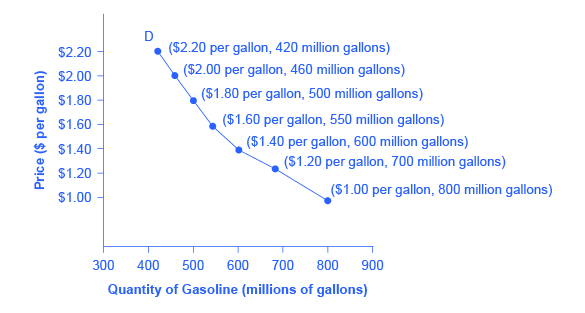
In the effort to maximize the utility of consumption consumers. The law of demand can be further illustrated by the demand schedule and the demand curve. In the definition the other things are the factors that influence the demand such as consumer s income price of related goods consumer s tastes and preferences advertisement etc.
The demand schedule is a tabular presentation of series of prices arranged in some. What does law of demand mean. It states that other things remain constant quantity demanded increases with a decrease in own price of commodity and vice versa.










:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ChangeInDemand2-bd35cddf1c084aa781398d1af6a6d754.png)

