Meaning Dominant Negative Effect

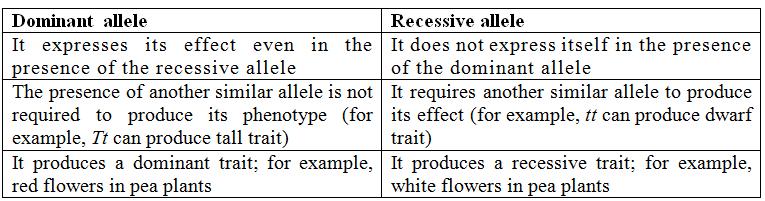
These mutations usually result in an altered molecular function often inactive and are characterized by a dominant or semi dominant phenotype.
Meaning dominant negative effect. Dominant mutations may be positive or negative occasionally a mutation causes a change of function or even a gain of function in the resulting gene product. Dominant negative mutations also called antimorphic mutations have an altered gene product that acts antagonistically to the wild type allele. In this case a single mutant copy of the gene may cause significant phenotypic effects that is the mutation is dominant.
An individual exhibiting such a change. A dominant negative effect may occur as a result of mutations that abrogate the activity of proteins that multimerize either with themselves or with other binding partners. Suppressor mutation the correction.
Dominant negative a mutation whose gene product adversely affects the normal wild type gene product within the same cell. This usually occurs if the product can still interact with the same elements as the wild type product but block some aspect of its function examples. Mcgraw hill dictionary of scientific.
The first variant is termed dominant and the second recessive this state of having two different variants of the same gene on each chromosome is originally caused by a mutation in one of the genes either. The dominant negative effect is defined as a circumstance in which a mutation occurs that results in a gene product adversely affecting wild type gene products all in the same cell. Point mutation a mutation resulting from a change in a single base pair in the dna molecule.
Somatic mutation a genetic mutation occurring in a somatic cell providing the basis for mosaicism. In genetics dominance is the phenomenon of one variant of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. Mutation resulting in a gene product that can interfere with the function of the normal gene product in heterozygotes.
Developmental biologists use the term dominant negative to describe a gene or protein which has a dominant effect similar to that described genetically i e. One copy of the gene gives a mutant phenotypic effect and a negative effect in that it prevents or has a negative impact on a biological process such as a signal transduction pathway. Explanation of dominant negative mutation.