Meaning Of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
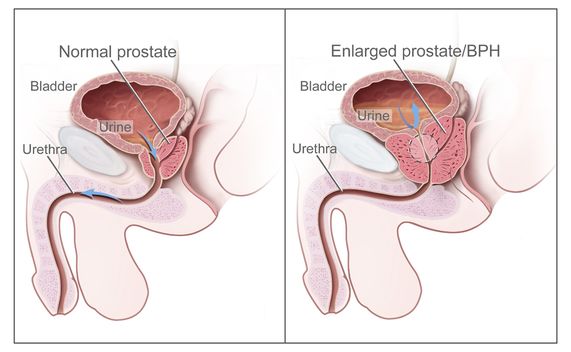
Benign prostatic hyperplasia definition is enlargement of the prostate gland caused by a benign overgrowth of chiefly glandular tissue that occurs especially in some men over 50 years old and that tends to obstruct urination by constricting the urethra abbreviation bph called also benign prostatic hypertrophy.
Meaning of benign prostatic hyperplasia. The first occurs early in puberty when the prostate doubles in size. It s a common problem for older men. An enlarged prostate gland can cause uncomfortable urinary symptoms such as blocking the flow of urine out of the bladder.
The second phase of growth begins around age 25 and continues during most of a man s life. Mean size of surgical prostatectomy specimens is 100 g usually in transitional and periurethral zones 5 in peripheral zone although enlarged prostate may compress other zones glandular hyperplasia is yellow pink soft oozing prostatic fluids stromal hyperplasia is gray tough. Define benign prostatic hyperplasia.
It can also cause bladder urinary tract or kidney problems. Abbreviated bph if bph is severe enough complete blockage can occur. It s a natural part of aging but at some point it can lead to a condition called bph or benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia synonyms benign prostatic hyperplasia pronunciation benign prostatic hyperplasia translation english dictionary definition of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Complications can include urinary tract infections bladder stones and chronic kidney problems. A nonmalignant enlargement of the prostate gland commonly occurring in men after the age of 50 and sometimes leading.
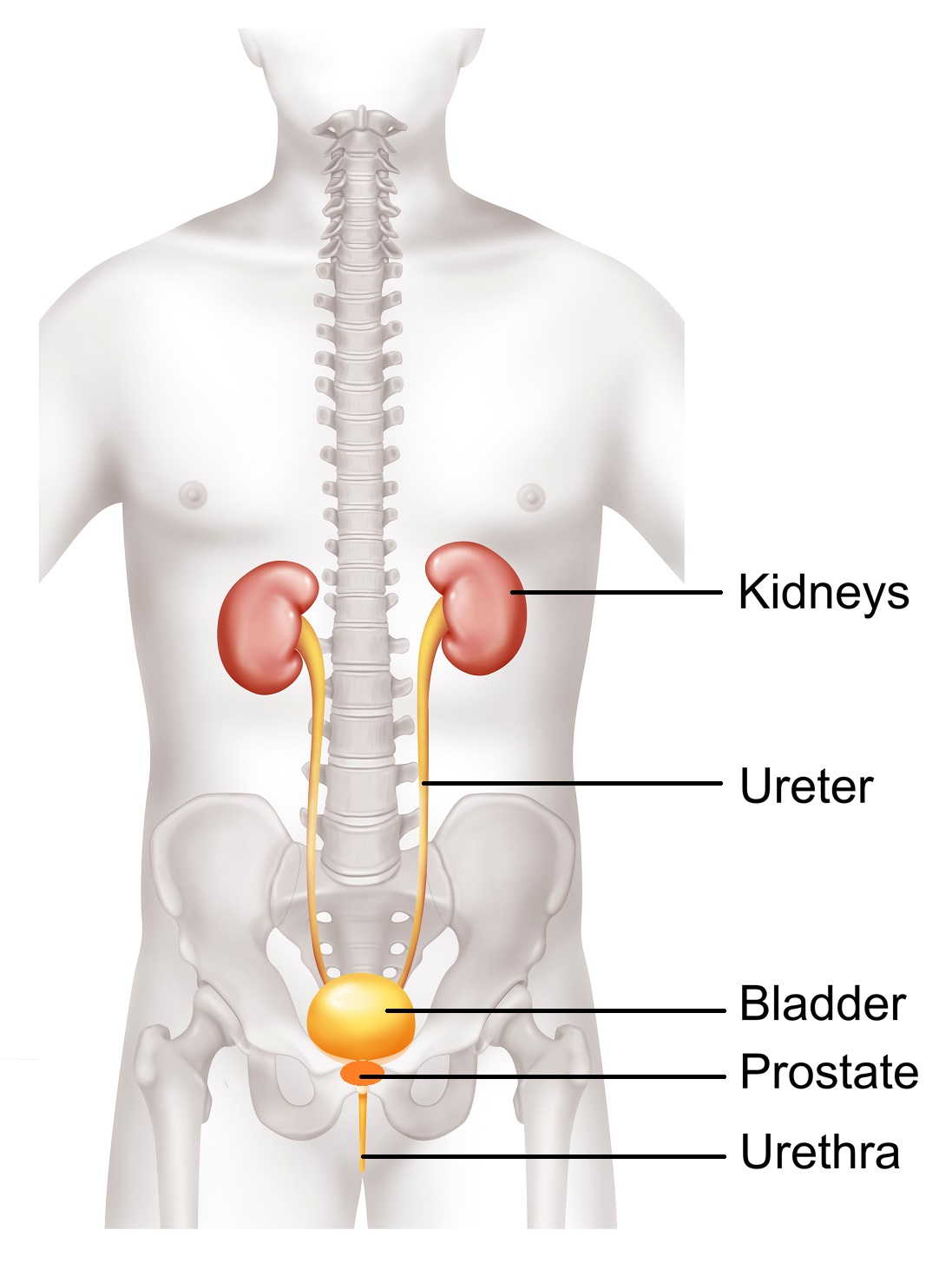
Your prostate surrounds part of your urethra the tube that carries urine. Benign prostatic hyperplasia or bph. Enlargement of the prostate gland.
Bph generally begins after age 30 evolves. Benign prostatic hyperplasia bph also called prostate gland enlargement is a common condition as men get older. A common noncancerous enlargement of the prostate gland the enlarged prostate may compress the urinary tube urethra which courses through the center of the prostate impeding the flow of urine from the bladder through the urethra to the outside.